5 Ideas for Cultivating a Growth Mindset in Students

What is Mindset?
Mindset is a set of beliefs that shape how we view the world and ourselves. The way we view the world – our mindset – affects how we grow, change, and bounce back from challenges. Try these 5 ideas to cultivate a growth mindset in your classroom and you’ll be amazed at the increased confidence and motivation with your students.
Why teach growth mindset?
Students who understand that the brain can get smarter – who have a growth mindset – excel in all areas because they have an empowering perspective on learning. They put forth a strong effort to focus on improvement and see mistakes, or even failure, as a natural part of the journey of learning. Check out our blog, Growth Mindset for Students, if you would like to learn more.
Fixed v. Growth Mindset
When our mindset is fixed, our thinking is rigid and our thoughts are often exaggerated, harsh or untrue. With a fixed mindset, it may be difficult to see the bigger picture and find solutions. A fixed mindset holds us back and keeps us stuck. We are mostly likely to fall into a fixed mindset when we are stressed, scared, or angry.
When we view the world from a growth mindset, our thinking is flexible and optimistic. We know that things can change over time by putting in effort, trying new strategies and surrounding ourselves with supportive friends. With a growth mindset, we see struggle as an opportunity. We can consider multiple solutions to a difficult problem and ask for support. It is easier to have a growth mindset we are happy, relaxed, and confident.
This video from YouCubed does a great job showing the differences between fixed and growth mindsets.
How to teach growth mindset in your classroom
1. Flip the script of negative self-talk. Introduce YET.
What we think matters and we all have thinking errors at times. Distortions or inaccurate thoughts can reinforce negative thinking and inhibit our growth mindset. The thoughts we think most often become hard-wired into our thinking. Help students analyze their thinking and learn to think and say words that build themselves up to make strong minds and bodies.
Examples:
- I can’t do this. → I can’t do this YET.
- I’m so bad at this. → I’m still learning and I’ll figure it out.
- I’m just not a math person → Anyone can learn math. I can too!”
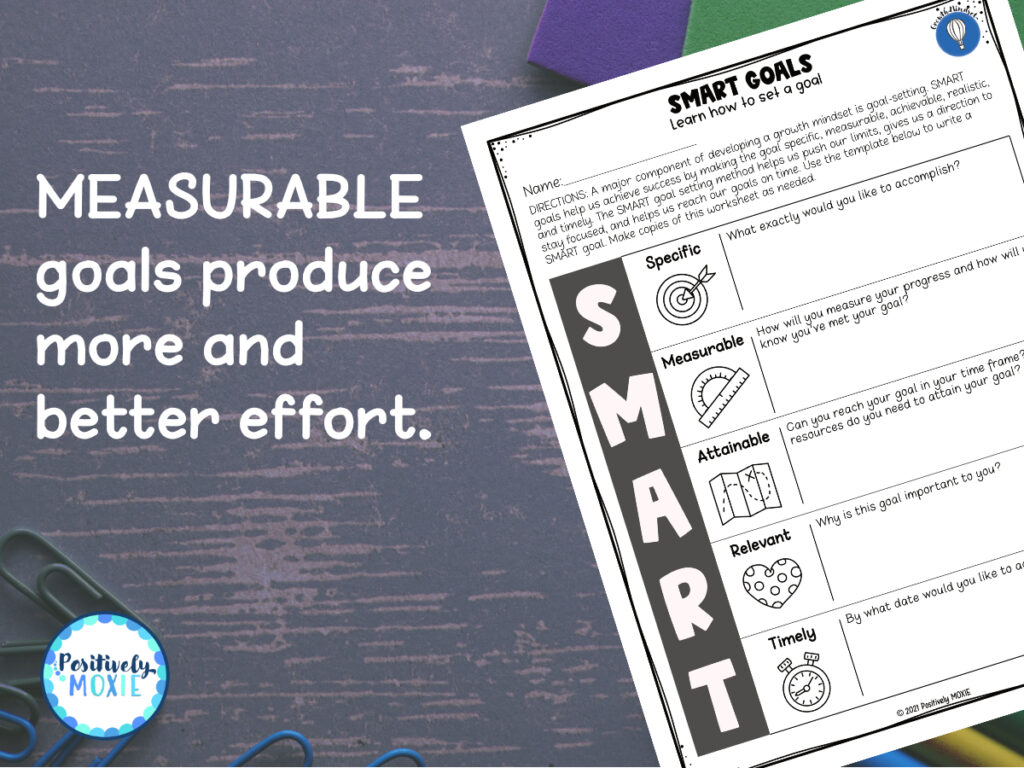
2. Set Goals
Learning how to set goals and creating an action plan for achieving them is also a key part of cultivating a growth mindset. Growth-mindset goals are uniquely actionable and focus on the small steps of growth because little changes in habits can lead to big changes in growth and achievement. Download your free SMART goals worksheet from this link.
3. Foster positive self-talk
Here’s a free poster to illustrate fixed versus growth mindset.

4. Normalize struggle and problem-solving.
There are many different types of problems in life – math problems, history problems, and even friendship problems. Problems are not good or bad,; they are just challenges for us to solve to keep moving forward. Learning to solve problems is important in building confidence and resilience.

5. View mistakes as part of the learning process.
Accepting responsibility for our choices and learning from our mistakes helps us grow. Mistakes become learning opportunities when we take the time to reflect on our actions.
- Reflect on the mistake with honesty and compassion. What were you thinking when you did it? How did your mistake affect other people?
- Reflect on any harm you caused. Did you hurt anyone’s feelings or inconvenience anyone? Do you need to apologize? What do you need to do to make thighs right?
Above all, be patient with yourself and students as you are moving toward a growth mindset. It is a journey that takes time. Enjoy the process and keep moving forward!
Our Growth Mindset products can help you nurture a growth mindset in your classroom.
Our Growth Mindset Bundle contains four complete lessons covering everything students need to know about growth mindset to help them on their journey. You can check it out at our TpT Store.