Using Sensory Areas to Help Students Regulate Their Behavior Using a Sensory Room

Creating a sensory room in an elementary school setting can be a game changer for students, especially those in special education. These thoughtfully designed spaces are not just about providing a break. They are crucial for helping students regulate their behavior, manage sensory overload, and optimize their learning potential. In this post, we’ll explore the three key areas within a sensory room: the Calming Area, Learning Area, and Active Area, and discuss how each can be utilized to support your students.
Calming Area
First, start with a calming area. This is a carefully designed space in the sensory room, offering a quiet retreat for students feeling overwhelmed. In a busy school, students with sensory sensitivities or emotional challenges can quickly become overloaded by noise and activity. The Calming Area gives them a much-needed break, helping them step away from the chaos. With soft lighting, cozy seating, and soothing tools like weighted blankets, noise-canceling headphones, and calming visuals, this area is meant to make students feel safe and at ease.
Furthermore, the Calming Area is crucial for students struggling to manage emotions or sensory input. It lets them take a break, self-soothe, and regain control. Whether escaping a tough situation or needing time to process their surroundings, this space offers a non-judgmental, supportive environment. Furthermore, It helps students calm down and teaches them self-regulation skills they can use beyond the sensory room, supporting their emotional and behavioral growth.
How Students Can Utilize the Calming Area:
- Weighted Blankets or Lap Pads: Students can use weighted blankets or lap pads while sitting in a cozy, low-light environment. The deep pressure provided by these tools can help ground students, reduce anxiety, and help them regain a sense of calm.
- Noise-Canceling Headphones and Soft Music: Noise-canceling headphones can be a lifesaver for students particularly sensitive to auditory stimuli. Pairing these with soft, calming music or white noise. This can help students block out the overwhelming classroom sounds, allowing them to focus on breathing and calming down.
- Bean Bag Chairs or Soft Seating: Offering bean bag chairs or other soft seating options gives students a comfortable place to sit and decompress. The sensory feedback from the soft materials can be soothing and help students settle their nervous system.
- Visual Relaxation Tools: Tools like lava lamps, bubble tubes, or fiber optic lights can provide calming visual stimulation. Watching these items’ slow, repetitive movements can help students examine their thoughts and relax.
- Breathing Exercises: Guided breathing exercises, perhaps with visual aids like breathing posters, can teach students how to manage their anxiety and stress by focusing on their breath.
Learning Area:
Next, establish an area for student learning. The Learning Area is a space designed to balance structure and flexibility. It helps with sensory regulation while encouraging focus and academic engagement. The goal is to give students the tools and settings that meet their sensory needs so they can concentrate without feeling overwhelmed. This space may have flexible seating like wobble stools, therapy balls, or floor cushions. These options let students move slightly as they learn, which helps those who struggle to sit still. The Learning Area ensures every student can succeed in a tailored environment by catering to different learning styles and sensory needs.
For students who struggle with focus, the Learning Area offers a controlled space where distractions are reduced and sensory inputs are managed. Visual schedules, task cards, and organized workstations create predictability, lowering anxiety and helping students stay focused. In addition, fidget tools, quiet activities, and sensory-friendly lighting can also channel extra energy or calm overstimulation. This space supports academic focus and teaches self-regulation, empowering students to take control of their learning and succeed in the classroom.
How Students Can Utilize the Learning Area:
- Flexible Seating Options: Incorporating seating options like wobble stools or therapy balls allows students to move while they learn. This strategy can help increase focus and decrease restlessness. Students who struggle to sit still may find that these seating options provide just the right amount of movement to stay engaged with their work.
- Fidget Tools and Quiet Activities: Providing fidget tools, like stress balls or fidget spinners, can help students with sensory needs stay engaged in their learning tasks. These tools allow students to release excess energy in a quiet, non-disruptive manner, making it easier for them to focus on their academic work.
- Visual Schedules: Displaying visual schedules or task lists can help students stay organized and reduce anxiety about transitions or tasks. Knowing what to expect can also help students focus on the current task.
- Task Cards or Work Bins: Offering task cards or organized work bins allows students to complete academic tasks in a structured, step-by-step manner. This approach can reduce feeling overwhelmed and help students stay on track with their learning.
- Quiet Reading Nook: A comfortable, quiet space with books or tablets for reading can provide a calming environment where students can engage in independent learning without distractions.
Active Area
Lastly, the Active Area, or Movement Area, is a key space in a sensory room. It helps students who need physical activity to regulate their sensory systems. In this area, students can do movement-based activities that provide the necessary proprioceptive and vestibular input. This helps them manage their energy and sensory experiences. It’s especially useful for students who struggle to sit still or get overstimulated. By offering safe, structured movement, the Active Area lets students release energy and refocus, making it easier for them to join classroom activities afterward.
For students who need frequent movement breaks, the Active Area is more than just a place to burn off energy; it’s a tool for self-regulation. For example, jumping on a mini-trampoline, navigating an obstacle course, or swinging help calm their nervous systems. These activities also help students feel more in control of their bodies. After using the Active Area, students can better focus, follow instructions, and engage in learning. The movement breaks let them channel their energy productively, supporting their overall well-being and success in the classroom.
How Students Can Utilize the Active Area:
- Obstacle Courses: Setting up a simple obstacle course with tunnels, balance beams, and stepping stones can give students the physical outlet they need. This activity helps regulate their sensory needs and improves coordination and motor skills.
- Jumping or Swinging Activities: Providing a mini-trampoline or itinerate swing in the active area allows students to engage in repetitive movements. This can be soothing and help reset their sensory system. A few minutes of jumping or swinging can help a student who is feeling unfocused return to the classroom, ready to learn.
- Wall Push-Ups or Resistance Bands: Activities like wall push-ups or resistance bands can help students release built-up energy in a structured way. These activities provide proprioceptive input, calming, and organizing for the body.
- Balance and Coordination Tools: Incorporating balance boards or therapy balls can help students develop balance and coordination while giving them the needed movement. These tools offer a controlled way for students to engage in physical activity.
- Interactive Sensory Walls: Sensory walls with different textures and activities can engage students in tactile exploration. These walls might include Velcro or soft fabric sections, allowing students to explore different sensations through touch.
8 Reasons Why Special Education Teachers Should Set Up a Sensory Room
1. Promotes Self-Regulation: A sensory room provides the tools and environment needed for students to learn how to self-regulate, an essential skill for managing behavior and emotions.
2. Reduces Classroom Disruptions: By giving students a designated space to manage their sensory needs, there are likely to be fewer disruptions in the classroom, leading to a more conducive learning environment for everyone.
3. Supports Diverse Learning Needs: Sensory rooms cater to a wide range of sensory needs, ensuring that all students, regardless of their sensory profile, have the support they need to succeed.
4. Enhances Focus and Attention: Providing spaces for sensory regulation can help students return to their classrooms more focused and ready to learn.
5. Encourages Independence: Sensory rooms empower students to recognize their sensory needs and take appropriate action, fostering independence and self-awareness.
6. Improves Social Skills: By reducing sensory overload, students are more likely to engage positively with peers and participate in group activities.
7. Supports Emotional Well-Being: A sensory room can be a refuge for students experiencing emotional difficulties, providing them with the space they need to process their feelings.
8. Facilitates Positive Behavior: Sensory rooms can help reduce negative behaviors and promote a more positive school experience by proactively addressing sensory needs.
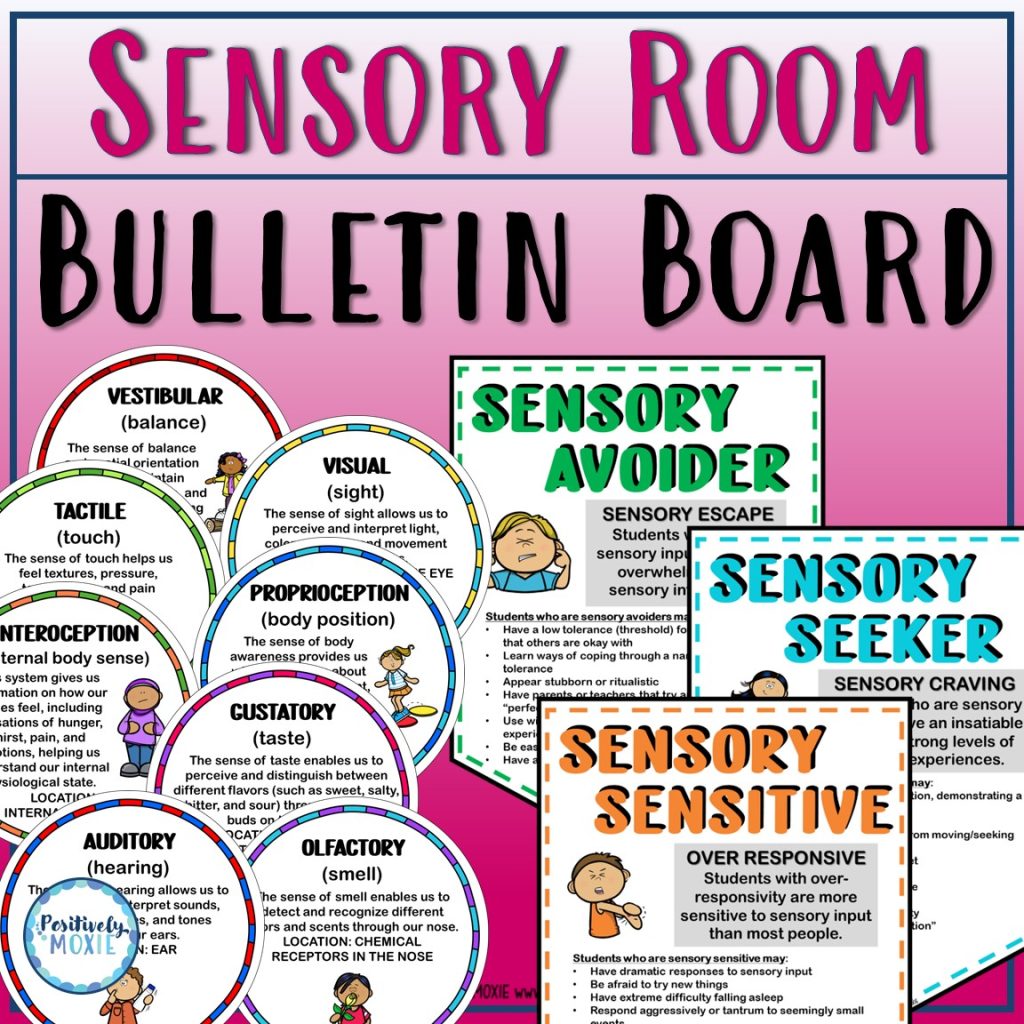
Sensory Room Bulletin Board
Enhance your sensory room using our comprehensive Sensory Room Bulletin Board Set. This product is designed to help you clearly define and organize your sensory spaces, ensuring that each area effectively serves its intended purpose.
This bulletin board set is an excellent resource for any special education teacher looking to create an organized, effective, and supportive sensory room.
In conclusion, creating a sensory room is an investment in your students’ well-being and learning potential. With the right setup, these spaces can significantly enhance how students manage their sensory needs, leading to better behavior, focus, and academic success.